What Are Parameterhttps://vizpulse.tech/understanding-parameters-in-tableau-data-analytics/s?
Parameters in Tableau are dynamic values that can replace constant values in calculations, filters, and reference lines. They allow users to interact with the data visualization by changing the parameter values, which in turn updates the visual representation of the data.
Why Use Parameters?
- Enhance Interactivity: Users can adjust the analysis by changing parameter values, leading to more customized insights.
- Perform “What-If” Analysis: Parameters make it possible to explore different scenarios without modifying the core data.
- Simplify Complex Calculations: They help in creating adjustable thresholds, such as setting custom targets or defining ranges.
- Improve User Experience: By allowing users to adjust values directly, parameters make dashboards more intuitive and user-friendly.
Types of Parameters
- Numeric Parameters: Used for numerical inputs like setting thresholds (e.g., sales targets) or choosing a numeric range for filtering.
- Example: A numeric parameter might allow a user to set a target sales number, adjusting a reference line on a sales chart.
2. String Parameters: Ideal for text-based inputs like selecting different categories or choosing between options.
- Example: A parameter could allow switching between “Product A,” “Product B,” or “Product C” in a visualization to see the performance of each product.
3. Date Parameters: Used for selecting specific dates or date ranges, ideal for time-based analysis.
- Example: A date parameter might let users choose a start and end date to filter a time series chart, such as analyzing data between specific months.
4. Boolean Parameters: Used for binary choices, such as true/false or yes/no selections.
- Example: A Boolean parameter could allow users to toggle the visibility of certain data elements in a dashboard, like showing or hiding a particular trend line.
How to Create a Parameter
- Go to the Data Pane: Right-click and select “Create Parameter.”
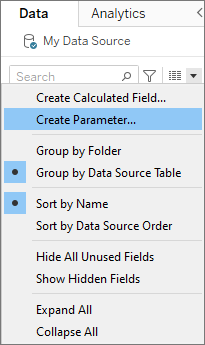
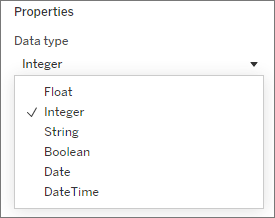
2. Define the Parameter: Assign a name, data type, and allowable values.
3. Use the Parameter: Integrate the parameter into calculated fields, filters, or as a reference line.



Example 1: Dynamic Sales Target
- Parameter Creation: Create an integer parameter named “Sales Target.”
- Calculated Field: Create a calculated field to compare actual sales with the sales target.
- Visualization: Display a bar chart with sales data and a reference line for the sales target.

Example 2: Adjustable Date Range
- Parameter Creation: Create two date parameters named “Start Date” and “End Date.”
- Calculated Field: Create a calculated field to filter data between the selected dates.
- Visualization: Show a line chart of sales over time with a date range filter controlled by the parameters.

Best Practices
- Default Values: Set meaningful default values for parameters to provide context.
- User Instructions: Include tooltips or text boxes to guide users on how to use the parameters.
- Performance: Be mindful of performance impacts when using complex calculations with parameters.
By incorporating parameters, Tableau users can create more interactive and customizable dashboards, enhancing the overall analytical experience.